class g airspace visibility requirements
Class E and Class G airspace. COC stands for Clear of Clouds.
How To Remember Vfr Weather Minimums Bobbie Lind
At night in Class G between 1200 AGL and 10000ft MSL the visibility and cloud clearance are the same as Class CD.

. 36 rows Notwithstanding the provisions of paragraph a of this section the following. On the other hand Class G airspace has four different sets of altitude-dependent minimums. In the airspace highlighted below Class E starts at 1200 AGL so Class G automatically starts at the surface and extends to - but doesnt include - 1200 AGL.
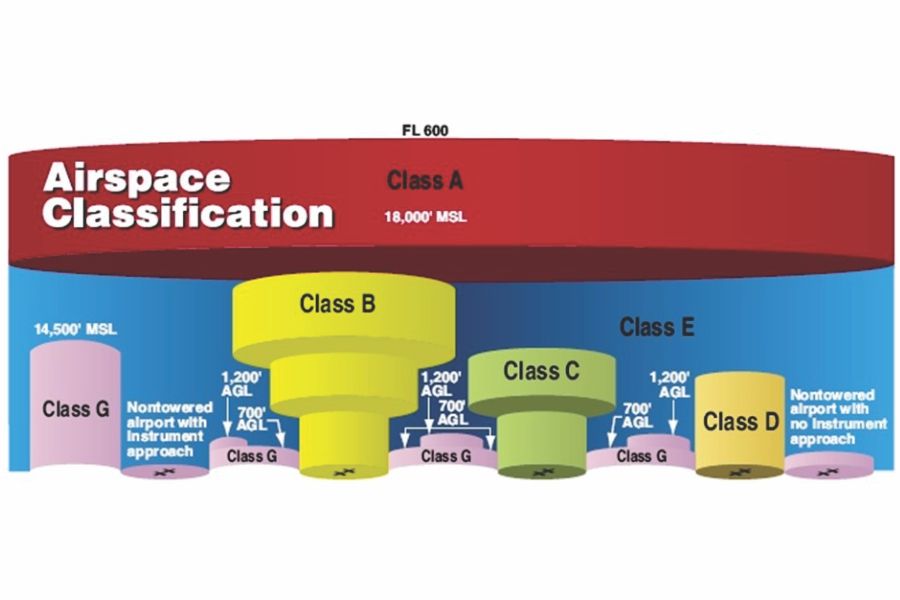
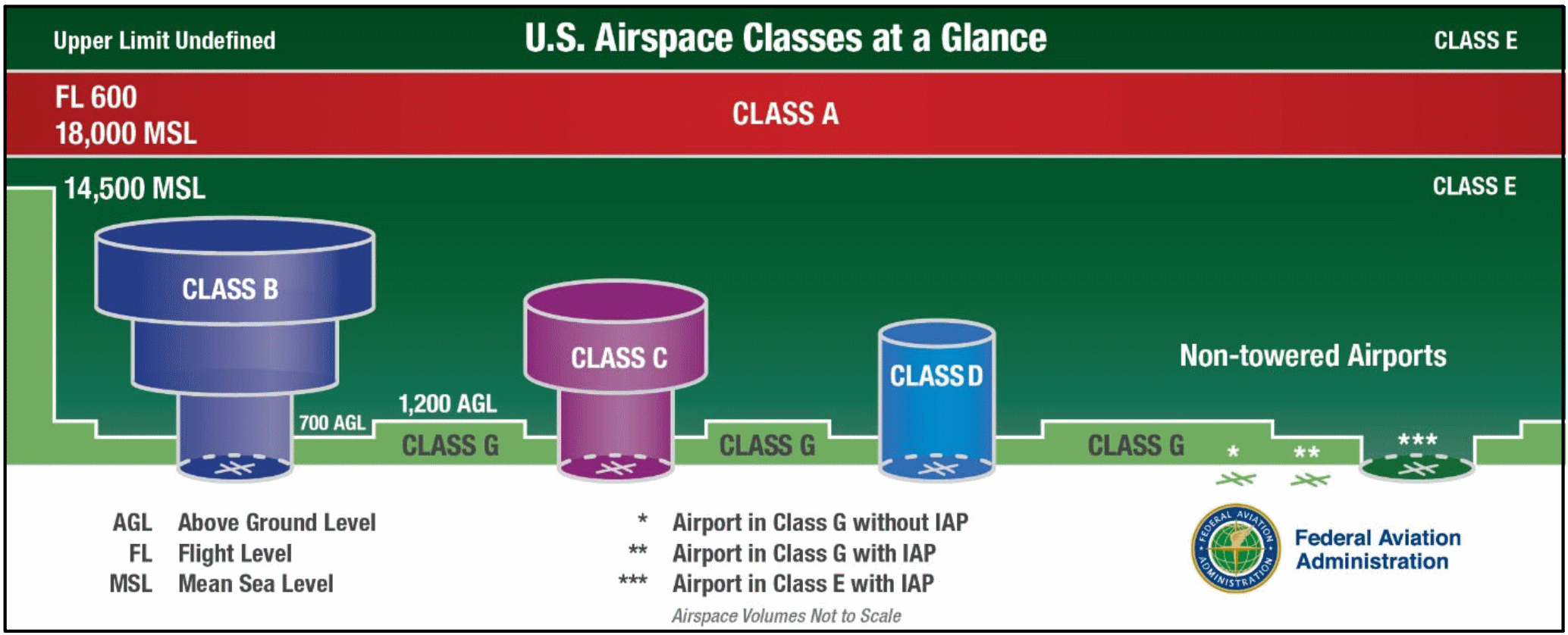
Although Class G is uncontrolled it is also subject to the most weather restrictions based on where the airspace is located. Related Article Class G Airspace Explained. Class A A for high Altitude or class alpha airspace exists from 18000 feet MSL up to 60000 feet MSL.
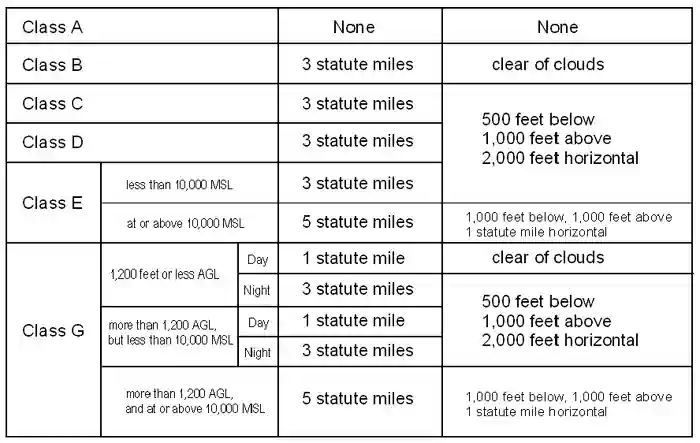
Above 10000ft MSL the requirements are 5 SM visibility and cloud clearance of 1000ft above 1000ft below and 1 SM horizontally. Rules governing VFR flight have been adopted to assist the pilot in meeting the responsibility to see and avoid other aircraft. 1200 feet or less above the surface regardless of MSL altitude 1 statute mile.
Class G airspace is not depicted on any chart. Weather Requirements Class G minimum weather requirements exist so that you can see and avoid other aircraft and stay out of the clouds. Altitude Range.
Uncontrolled airspace is designated as Class G with areas having low volume of air traffic. A Unless otherwise specified in the certificate holders operations specifications when conducting VFR helicopter air ambulance operations in Class G airspace the weather minimums in the following table apply. Minimum flight visibility and distance from clouds required for VFR flight are contained in 14.
Daytime requirements for Class G are 1 statute mile visibility and clear of clouds to 1200ft. Day except as provided in 91155 b 1 statute mile. 135609 VFR ceiling and visibility requirements for Class G airspace.
Above the Class G ground is Class E everywhere else and is controlled airspace. VFR Minimum Distance from Clouds Below 10000 MSL. 1200 or less above the surface regardless of MSL altitude Flight Visibility.
VFR Minimum Visibility Below 10000 MSL. Sport and recreational aviation activities. Visibility requirements also tend to increase above 10000 MSL because as noted later above this altitude aircraft are authorized to travel at much higher airspeeds and need to see aircraft in time which means at an increased distance to see and avoid them in VFR Visual Flight Rules.
One mile visibility and clear of clouds is the daytime requirement. Air Traffic Control Facility. 10 rows G night 3 statute miles 152 4500 below 41000 above 42000 horizontal G day 1 statute mile.
500 Below 1000 Above 2000 Horizontal. Class G Airspace Weather Visibility Requirements. 1200ft or less above the surface regardless of MSL altitude Day.
Class D is a single cylindrical area extending from the surface to 2500 feet agl. In summary Class G Airspace is the least restrictive of all airspaces. 500 Below 1000 Above 2000 Horizontal 500 Below 1000 Above.
14 rows These minimums cover most Class G airspace but are only valid during the daytime when you are. 500 Below 1000 Above 2000 Horizontal. Day - 1 Statute Mile Night - 3 Statute Miles.
There are moderate required VFR weather minimums. Visibility and cloud clearance requirements are less as well like in class G airspace. Most air traffic in Class G fly under Visual Flight Rules VFR rules.
In accordance with FAR 91155. Class G airspace uncontrolled is that portion of airspace that has not been designated as Class A Class B Class C Class D or Class E airspace. Only IFR aircraft are permitted in class A airspace and air traffic control is responsible for ensuring their separation both vertically and horizontally.
For aircraft other. Class G communications. Above 1200ft stays at 1sm visibility but then for cloud clearance you must be 1000ft above 500ft below and 2000ft horizontal.
To prepare for flying in Class D airspace simply learn what Class D airspace is where it is located what the operational requirements and restrictions are and how to get approval to enter. If underneath Class B or C airspace Class D. Class G 1200 feet or less above the surface regardless of MSL altitude.
Night minimums in Class G Airspace remain the same regardless of altitude. Above that altitude Class G Airspace weather minimums increase to one statute mile visibility while remaining 500 feet below clouds 1000 feet above clouds and 2000 feet horizontally from clouds. Requirements for a flying in a Class D airspace are relatively minor and obtaining approval to enter is also very simple once you know what to do.
1200 feet or less above the surface regardless of MSL altitude For aircraft other than helicopters. 1 statute mile visibility and clear of clouds. You can remember Class G uncontrolled airspace because its just like the good old days at the dawn of aviation.
Night except as provided in 91155 b 3 statute miles. At night requirements jump to three miles visibility and from merely clear of clouds to 500 feet below 2000 feet horizontal and. Air defence identification zone.
Also there are no communication or air traffic control requirements. It is the pilots responsibility to see and avoid other traffic.
How To Remember Vfr Weather Minimums Bobbie Lind

Aviation Humor Aviation Quotes Aviation Humor Aviation Humor Pilots

Helicopter Instrument Procedures Part Three
Regulations Vfr Minimums Learn To Fly Blog Asa Aviation Supplies Academics Inc

In The Book Air Operations In East Timor By Hendro Subroto The Air Force Via The Air 2 Angkut Ringan Squadron Operated Two Ac 47 Units In The Seroja Lotus

Uncontrolled And Controlled Airspace

Faa Airspace For Vfr Flight Youtube

Sectional Airspace Summary Pilotvintage Aviation Classes Student Pilot Flight Lessons
How To Remember Vfr Weather Minimums Bobbie Lind

Airspace Classes Explained The Ultimate Guide For Beginners

How To Memorize Things Flight Training Ground School

Sectional Chart Airspace Classification Overview Aerial Guide Chart Classification Cardinal Directions